The user can control how protocols are dissected.
Each protocol has its own dissector, so dissecting a complete packet will typically involve several dissectors. As Wireshark tries to find the right dissector for each packet (using static “routes” and heuristics “guessing”), it might choose the wrong dissector in your specific case. For example, Wireshark won’t know if you use a common protocol on an uncommon TCP port, e.g., using HTTP on TCP port 800 instead of the standard port 80.
There are two ways to control the relations between protocol dissectors: disable a protocol dissector completely or temporarily divert the way Wireshark calls the dissectors.
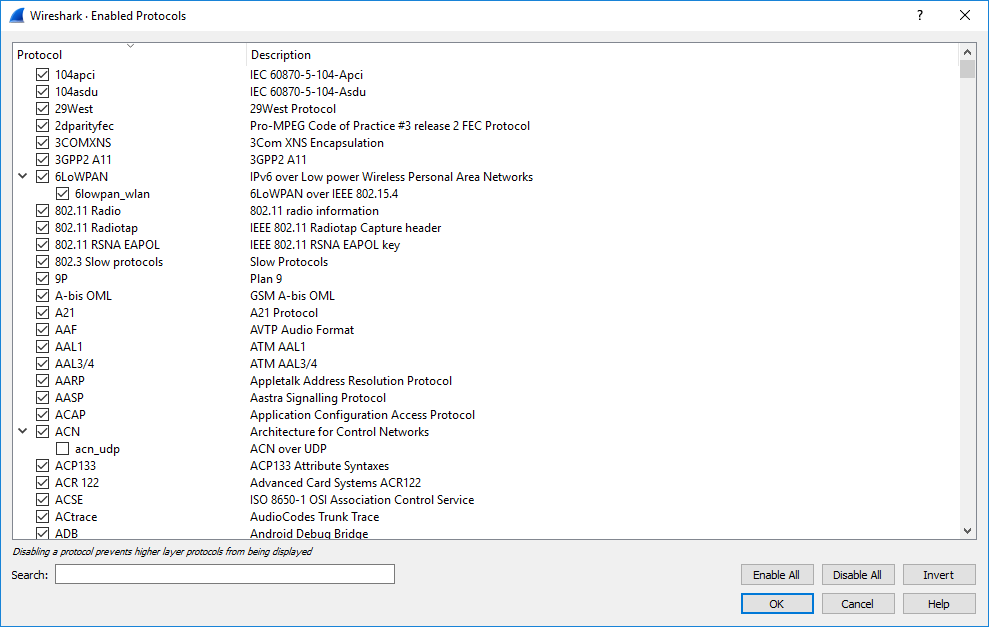
The Enabled Protocols dialog box lets you enable or disable specific protocols. Most protocols are enabled by default. When a protocol is disabled, Wireshark stops processing a packet whenever that protocol is encountered.
| Note | |
|---|---|
|
Disabling a protocol will prevent information about higher-layer protocols from being displayed. For example, suppose you disabled the IP protocol and selected a packet containing Ethernet, IP, TCP, and HTTP information. The Ethernet information would be displayed, but the IP, TCP and HTTP information would not - disabling IP would prevent it and the higher-layer protocols from being displayed. |
To enable or disable protocols select → . Wireshark will pop up the “Enabled Protocols” dialog box as shown in Figure 11.4, “The “Enabled Protocols” dialog box”.
To disable or enable a protocol, simply click the checkbox using the mouse. Note that typing a few letters of the protocol name in the search box will limit the list to those protocols that contain these letters.
You can choose from the following actions:
- Enable all protocols in the list.
- Disable all protocols in the list.
- Toggle the state of all protocols in the list.
- Save and apply the changes and close the dialog box, see Section A.2.4, “[Stream setup by PROTOCOL (frame 123)]” for details.
- Cancel the changes and close the dialog box.
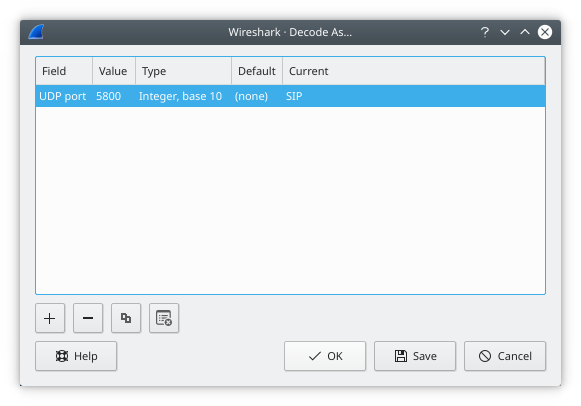
The “Decode As” functionality lets you override what protocol is called under specific circumstances. This might be useful if Wireshark is incorrectly choosing which dissector to use for a particular TCP port, for example, or if you do some uncommon experiments on your network.
| Note | |
|---|---|
|
Not all protocols support this feature, and not just any protocol field can be used to override Wireshark’s choice of dissector. |
Decode As is accessed by selecting the → . Wireshark will pop up the “Decode As” dialog box as shown in Figure 11.5, “The “Decode As” dialog box”.
In this dialog you are able to edit entries by means of the edit buttons on the left.
You can also pop up this dialog box from the context menu in the “Packet List” or “Packet Details” panes. It will then contain a new line based on the currently selected packet.
These settings will be lost if you quit Wireshark or change profile unless you save the entries.
- Add new entry for selected packet
- Remove the selected entry.
- Copy the selected entry.
- Clear the list of user specified decodes.
- Apply the user specified decodes and close the dialog box.
- Save and apply the user specified decodes and close the dialog box.
- Cancel the changes and close the dialog box.
Each entry in this dialog will have the following columns. You can double-click on an entry’s field to change its value, as long as it’s not an informational (read-only) field.
| Heading | Description |
|---|---|
Field | The field whose value should be examined when determining the dissector to use. Double-click to show a list of all fields which are supported for this feature. |
Value | The specific value of the chosen field which should indicate to Wireshark to use your chosen dissector override. |
Type | Read-only. Shows the type of the chosen field’s value; for example, integer or string. |
Default | Read-only. Shows what dissector would normally be called if the chosen field had the chosen value. |
Current | The dissector you wish to be called instead. You will only be able to choose dissectors for protocols which could be directly carried by the containing protocol. For example, you cannot specify that data carried over TCP should be passed to the Ethernet dissector. |
| Tip | |
|---|---|
|
You can also specify “Decode As” entries on the Wireshark or tshark
command line. See the documentation of the |